Pathophysiology of CAD
(Pathophysiology means a disease process
CAD means coronary artery disease where the arteries
Supporting blood to the heart become narrowed or
Blocked due to a plaque( involves build up of fatty deposits
Of cholesterol and other substances within artery wall.)
Coronary artery disease is typically caused
by atheromatous constriction of the vessel and subsequent blockage. From young adulthood onwards, early atheromatous plaque (derived from the Greek word; Athera - porridge and Oma - lump) is evident. A mature plaque comprises two components that are
macrophages (also called big eaters)
and smooth muscle cells, each of which belongs to a particular cell lineage [11]. The necrotic "foam cells"
- monocyte-derived macrophages that move
into the intima
(Inner lining of blood vessels)
of and absorb lipids - are the primary source
of the lipid core. Smooth muscle cells
migrate in the vascular wall from the media into the intima, where they multiply and change their phenotype (to create a fibrous capsule around the lipid core, forming the connective tissue matrix [11]. Calcification of the
coronary arteries occurs in tandem with the progression of severe atherosclerosis( atherosclerosis is
thickening or hardening of arteries caused by building of plaque in the inner lining
Of an artery)
Risk factors
1 High cholesterol
2Triglycerides
3High BP
4Smoking
5Diabetes)
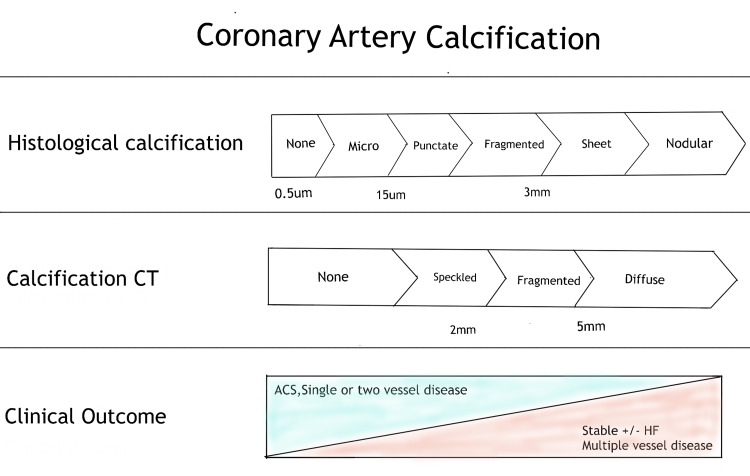
. Calcification usually begins as
micro-nodules (0.5 to 15.0 μm) and later progress to larger calcium particles which form sheets like
deposition (>3mm) in the arteries.
These changes appear to take place concurrently
with plaque evolution (Figure 1) [12]. Coronary artery stenosis of more than 50% or a reduction in the cross-sectional area by 80% usually leads to angina on exertion. Intimal damage causes thrombus development by causing denudation of the thrombogenic matrix or lipid pool. Occlusion is more complete in acute myocardial infarction than unstable angina, where arterial occlusion is frequently partial. Acute coronary events usually occur when a plaque ruptures and triggers the formation of a thrombus [11].
Figure 1. Coronary artery calcification.
Various factors have a role in the onset
and advancement of calcification,
which vary depending on the stage of plaque and the surrounding environment. Although
it is usually associated with aging, various
factors, including numerous associated risk factors that can accelerate the calcification in atheromatous plaques like environmental, genetic, family history, and lifestyle accounting for early CAD.
Ref
Cureus
. 2021 Dec Figure 1. Coronary artery calcificatiFigure 1
CT(12):e20149. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20149
Coronary Artery Calcium Score - A Reliable Indicator of Coronary Artery Disease?
Devarashetty Shreya 1,✉, Diana I Zamora 2, Gautami S Patel 3, Idan Grossmann 4, Kevin Rodriguez 5, Mridul Soni 6, Pranay K Joshi 7, Saawan C Patel 3, Ibrahim Sange 8,9
Editors: Alexander Muacevic, John R Adler
No comments:
Post a Comment